Climate change forces Panama islanders to relocate
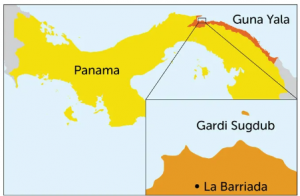
- Concerns over rising sea levels forced roughly 300 families on the island of Gardi Sugdub in the Guna Yala province of Panama to migrate at the beginning of June.
What’s going on in the Gardi Sugdub?
- Location and Community: Located in the Guna Yala province of Panama, Gardi Sugdub is an island inhabited by approximately 1,300 members of the Guna community.
- Sea Level Rise: The Caribbean region, which includes Panama, is seeing an average annual increase in sea level of three to four millimeters. By 2100, this rate should have accelerated to at least one centimeter annually.
- Flooding: Despite efforts to secure the island, seawater floods Gardi Sugdub’s residences and streets every year, especially in November and December.
- Relocation: To assist impacted residents in moving, the Panamanian government built 300 new homes in a neighborhood known as Nuevo Cartí on the mainland.
How are other island nations affected by sea level rise?
- Small island developing states (SIDS) are more susceptible because of their dependence on marine resources and low elevation. Rising sea levels pose existential concerns to SIDS in the Caribbean, Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, and South China seas.
- Examples of Impact: Threats to the cultures and economy of islands like Kiribati, Tuvalu, and the Marshall Islands, as well as substantial land loss, are occurring.
- The consequences of rising sea levels, storm surges, and “king tides” include coastal erosion, salinization of freshwater resources, and greater susceptibility to extreme weather events.
How quickly is the sea level increasing globally?
- Global sea levels have risen by about 21–24 millimeters since 1880. In recent decades, the rate of increase has quickened.
- Reasons: The melting of land-based ice, including glaciers and ice sheets, thermal expansion of ocean, and global warming are the main causes.
- Because of the Rise in Global Temperature: Sea levels are increasing as a result of the minimum 1.1 degree Celsius increase in the world’s average temperature since 1880.
Way forward:
- Boost Environmental and Coastal Defenses: To fend off storm surges and coastal erosion, build breakwaters, seawalls, and other obstacles. To improve natural protection, restore and maintain natural coastal barriers including mangroves, coral reefs, and wetlands.
- Create and Put into Practice Climate Adaptation Strategies: Make thorough preparations for climate adaptation that include vulnerable groups’ relocation needs.
Explain the causes and effects of coastal erosion in India. What are the available coastal management techniques for combating the hazard? (2022)
Why Denmark has taxed cattle burps and farts?
Denmark’s Livestock GHG Tax (2020)
Overview:
- Denmark to impose a tax on livestock farmers for greenhouse gases (GHGs) emitted by cows, sheep, and pigs starting in 2030.
Tax Rates:
- Initial rate: $43 per metric ton of carbon dioxide equivalent in 2030.
- Increased rate: $108 per metric ton by 2035.
- Actual cost after 60% income tax deduction:
- 120 kroner ($17.3) per ton in 2030.
- 300 kroner ($43) per ton by 2035.
Use of Tax Collection:
- Funds collected between 2030 and 2031 will be reinvested in the industry to support its green transition.
- Handling of proceeds to be revisited in 2032.
- Proposal includes developing over 600,000 acres of new forest areas.
Methane Production by Livestock:
- Ruminants (cows, sheep, goats, buffaloes) have a specialized digestive system with four stomach compartments.
- Methane is produced in the rumen during the fermentation of partially digested food.
- Methane is released through burping and farting as animals regurgitate and chew cud.
- Ruminants are responsible for 27% of methane emissions from human activity.
Methane Emissions Concerns:
- Climate Impact: Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, responsible for 30% of warming since preindustrial times, and is 80 times more potent than carbon dioxide over a 20-year period.
- Ground-Level Ozone: Methane contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone, leading to 1 million premature deaths annually.
- Rising Levels: Atmospheric methane levels have dramatically increased, with a record 17 parts per billion increase reported by NOAA in 2021.
Way Forward:
- Dietary Adjustments: Introduce feed additives (e.g., seaweed) to reduce methane emissions during digestion without impacting livestock health or productivity.
- Improved Manure Management: Use advanced manure management practices (e.g., anaerobic digestion) to capture and convert methane from animal waste into biogas, reducing emissions and providing renewable energy.
Describe the major outcomes of the 26th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). What are the commitments made by India in this conference? (2021)
UNESCO World Heritage Site of Somanathapura

Karnataka’s Tourism Highlight: Somanathapura Temple
Overview:
- Karnataka’s Tourism Department plans to promote Somanathapura Temple in the Mysuru tourism circuit ahead of Dasara.
- Focus on its UNESCO World Heritage status, granted in September 2023 as part of the ‘Sacred Ensembles of the Hoysala,’ which includes Chennakeshava Temple at Belur and Hoysaleshwara Temple at Halebid.
Keshava Temple, Somanathapura:
- One of the last grand structures of the Hoysala dynasty.
- A Trikuta (three-shrined) temple dedicated to Lord Krishna in three forms: Janardhana, Keshava, and Venugopala.
- The main Keshava idol is missing; Janardhana and Venugopala idols are damaged.
Historical Background:
- Built by Somanatha, a Hoysala Army commander, during the reign of King Narasimha III.
- Somanatha established the town of Somanathapura and sought the king’s permission and resources for the temple’s construction.
- Construction began with the king’s blessing and was completed in 1268 AD.
- Inscription in old Kannada on a stone slab provides construction and consecration details.
- No longer serves as a place of worship due to demolitions by invaders.
Architecture:
- Constructed from soapstone, allowing for fine detailing in carvings.
- Built on a raised platform with an outer Pradakshina pathway for circumambulation.
- Features a stellar (star-shaped) plan with multiple corners and niches for intricate sculptures.
- Each of the three shrines is crowned with a Vimana (tower).
- Displays the Hoysala emblem of a warrior fighting a lion.
- Walls adorned with friezes depicting scenes from Hindu epics, elephants, and battle scenes with cavalry.
The Nagara, the Dravida and the Vesara are the: (2012)
(a) three main racial groups of the Indian subcontinent
(b) three main linguistic divisions into which the languages of India can be classified
(c) three main styles of Indian temple architecture
(d) three main musical Gharanas prevalent in India
Geoportals for Enhanced Rural Land Records and Emergency Management
Launch of Geoportals by the Union Ministry of Science and Technology
Overview:
- Two Geoportals launched: ‘Bhuvan Panchayat (Ver. 4.0)’ and ‘National Database for Emergency Management (NDEM Ver. 5.0)’.
- Developed by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO).
- Provide high-resolution satellite imagery at a 1:10K scale across the country.
Bhuvan Panchayat (Ver. 4.0):
- Supports “Space-based Information Support for Decentralized Planning (SISDP)”.
- Empowers grassroots citizens by providing real-time land record data.
- Reduces dependency on local administration and curtails corruption.
- Promotes ease of living through digitalization and better land revenue management.
- Enhances transparency and efficiency in land record management.
- Aids in effective governance and planning.
National Database for Emergency Management (NDEM Ver. 5.0):
- Provides space-based inputs on natural disasters, aiding disaster risk reduction.
- Establishes an effective early warning system for disaster prevention and land use monitoring.
- Features a command centre to continuously monitor situations and provide inputs.
- Designed to assist both India and neighbouring countries in disaster management.
- Enhances coordination between various agencies and local authorities for effective disaster response and management.
-
Daily Current Affairs - 23rd January 2025
-
Daily Current Affairs - 22nd January 2025
-
Daily Current Affairs - 21st January 2025
-
Daily Current Affairs - 18th January 2025
-
Daily Current Affairs - 16th January 2025
-
Daily Current Affairs - 15th January 2025
-
Daily Current Affairs - 14th January 2025
-
Daily Current Affairs - 13th January 2025
Categories
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | |||
