On the Jurisdiction of the CBI
Supreme Court Verdict on West Bengal Government’s Suit Against Union Government
Background
- Withdrawal of Consent: West Bengal government withdrew “general consent” for CBI investigations on November 16, 2018.
- Continued Investigations: CBI continued to register FIRs and investigate cases in West Bengal.
- Legal Action: West Bengal filed a suit in the Supreme Court under Article 131, accusing the Union government of “constitutional overreach.”
Key Highlights of the Verdict
- Solicitor-General’s Argument: Tushar Mehta argued for CBI’s independence from the Union government.
- Supreme Court’s Ruling: CBI is not entirely independent; it operates under the DSPE Act, 1946.
- Central Government Control: The central government controls CBI’s establishment and administration, except for cases under the Prevention of Corruption Act (supervised by the CVC).
Independence of CBI
- Constitution and Administration: CBI constituted and administered under the DSPE Act, 1946.
- Superintendence: Central government oversees CBI, especially for non-corruption cases.
- Union Government’s Role: Vital involvement in CBI’s functions and operations.
CBI’s Authority in States
- DSPE Act Provisions: CBI derives powers from DSPE Act, 1946; needs state government consent for investigations beyond Union Territories.
- Supreme Court Ruling: State consent is required despite CBI being under Union government’s control.
Types of Consent
- General Consent: No need for CBI to seek permission for each case.
- Specific Consent: Required on a case-by-case basis if general consent is withdrawn.
- Withdrawal of General Consent: Several states (Mizoram, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Punjab, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Kerala, Jharkhand, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Meghalaya) have withdrawn general consent, impacting CBI’s operations.
- Pending Investigations: Withdrawal of consent does not affect ongoing investigations or court-ordered probes. CBI can obtain search warrants from local courts in states without general consent.
The jurisdiction of the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) regarding lodging an FIR and conducting probe within a particular State is being questioned by various States. However, the power of the States to withhold consent to the CBI is not absolute. Explain with special reference to the federal character of India. (2021)
The SC ruling on the portrayal of disability in films
Supreme Court Guidelines Against Stereotyping Persons with Disabilities in Visual Media
Background
- Plea: Activist Nipun Malhotra filed a plea against the film ‘Aaankh Micholi’ for allegedly insensitive portrayal of differently-abled individuals.
- Petitioner’s Argument: The film contained derogatory references and stereotypes about persons with disabilities.
Key Highlights of the Supreme Court Ruling
- Avoiding Derogatory Language:
- Creators should avoid terms like “cripple,” “spastic,” “afflicted,” “suffering,” and “victim” as they promote negative self-image and discrimination.
- Accurate Representation:
- Creators must end the stereotyping of differently-abled persons and ensure accurate representation of disabilities.
- Involvement of Persons with Disabilities:
- Adhere to the principle of “nothing about us, without us” by involving persons with disabilities in content creation and assessment.
- Training and Collaboration:
- Implement training programs for writers, directors, producers, and actors to sensitize them about the impact of their portrayals on public perceptions.
Laws Granting Disability Rights
- Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Act, 2016:
- Primary legislation addressing rights and entitlements of persons with disabilities, replacing the 1995 Act.
- National Trust Act, 1999:
- Provides legal support and guardianship for persons with autism, cerebral palsy, mental retardation, and multiple disabilities.
- Rehabilitation Council of India Act, 1992:
- Regulates training of rehabilitation professionals and promotes research in rehabilitation and special education.
- Mental Healthcare Act, 2017:
- Includes provisions related to the rights and treatment of persons with mental disabilities, focusing on mental health issues.
Implementation of Disability Rights Laws
- Implementation Gaps:
- Significant discrepancies exist between legal provisions and their practical implementation; many disabled persons face barriers in accessing their rights.
- Awareness and Sensitization:
- General public and government bodies often lack awareness about the rights and needs of persons with disabilities.
- Infrastructure and Accessibility:
- Despite legal mandates, accessibility in public places, transportation, and buildings is unevenly implemented.
- Employment Opportunities:
- Mandated employment quotas for persons with disabilities in government and private sectors are often unmet.
Way Forward
- Enhanced Monitoring and Accountability:
- Implement regular audits and monitoring to ensure compliance with disability rights laws across all governance levels and sectors.
- Increased Awareness and Sensitization:
- Launch nationwide awareness campaigns targeting the general public and stakeholders in government and private sectors to promote understanding of disability rights.
The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 remains only a legal document without intense sensitisation of government functionaries and citizens regarding disability. Comment. (2022)
Ratna Bhandar of Puri Jagannath Temple, opened after 46 years
Reopening of Shree Jagannath Temple’s Ratna Bhandar After 46 Years
About the Ratna Bhandar
- Treasury Contents: Stores gold and jewels offered by devotees to Lord Jagannath, Lord Balabhadra, and Goddess Subhadra.
- Location: Adjacent to the prayer hall on the north side of the temple.
- Sections:
- Bhitar Bhandar (Inner Treasury)
- Bahar Bhandar (Outer Treasury)
- Last Inventory (1978): Significant amounts of gold and silver items noted.
- Historical Legend: King Anangabhima Dev (1211-1238) is said to have donated 2.5 lakh madhas of gold for jewellery.
- Management Act: Odisha government passed the Jagannath Temple Act, 1952 for better management, including maintaining an inventory of offerings.
Recent Developments
- Management Committee: Chaired by the titular ‘King of Puri’, includes IAS officers and state-appointed members.
- Key Holders: Originally held by the Puri royal family, temple committee, and collectorate. Changes in ownership and access protocols due to legal rulings.
- Reopening Process: Involved breaking the locks of the inner chamber due to inability to open traditionally, following strict procedures.
About Jagannath Puri Temple
- Significance: Important Vaishnavite temple dedicated to Jagannath, a form of Sri Krishna.
- Historical Rebuilding: Rebuilt from the 10th century onwards, begun by Anantavarman Chodaganga Deva, the first king of the Eastern Ganga dynasty.
- Annual Festival: Famous for the Ratha Yatra (chariot festival), where the three principal deities are pulled on large, elaborately decorated temple cars.
Architecture of Jagannath Puri Temple
- Architectural Style: Rich sculptural Oriya style, considered one of the most magnificent monuments in India.
- Complex Area: Covers over 400,000 square feet.
- Fortified Walls:
- Meghanada Pacheri: 20 feet high wall surrounding the temple complex.
- Kurma Bedha: Another wall surrounding the main temple.
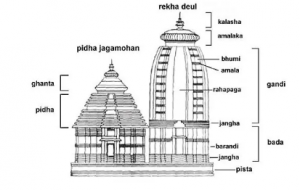
Four Distinct Sectional Structures
- Deula (Vimana or Garba Griha):
- Function: Sanctum sanctorum where the triad deities are lodged on the ratnavedi (Throne of Pearls).
- Style: Rekha Deula.
- Mukhashala:
- Function: Frontal porch.
- Nata Mandir/Natamandapa (Jagamohan):
- Function: Audience Hall/Dancing Hall.
- Bhoga Mandapa:
- Function: Offerings Hall.
UMLING LA
Testing of UAV at Umling La Pass by Bengaluru-Based Firm
Key Points
- Testing: Successfully tested a 100-kg Max Take Off Weight (MTOW) Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) at Umling La pass, Ladakh.
- Potential Benefits:
- Logistics Support: Enhances logistics carriage capabilities in high-altitude regions.
- Disaster and Rescue: Improves efficiency in disaster and rescue operations.
- Medical Relief: Facilitates medical relief efforts in remote and higher regions of J&K, Uttarakhand, and the North Eastern states.
About Umling La Pass
- Location: Ladakh, India.
- Significance: Highest paved road and mountain pass in the world.
- Altitude:
- Pass height: 5799 meters (19,024 feet).
- Higher than Everest Base Camp and over half the cruising altitude of commercial jet airlines.
Chisumle-Demchok Road (Umling La Road)
- Construction:
- Built By: Border Roads Organization of India.
- Length: 52 kilometers.
- Route: Connects the villages of Chisumle and Demchok.
- Record: Surpassed the previous record held by the 18,953-foot Uturuncu volcano road in Bolivia, becoming the world’s highest motorable road and pass.
Project Himank
- Achievement: The Border Roads Organization (BRO) accomplished this feat as part of “Project Himank.”
MACKENZIE RIVER
Record-Low Water Levels in the Mackenzie River
Background
- Current Situation: The Mackenzie River is experiencing record-low water levels.
- Causes:
- Extreme Hot Conditions: Unusually high temperatures.
- Low Precipitation: Very little rainfall leading to significant evaporation.
- Impact on Local Communities:
- Transportation: Disruption in river-based transportation.
- Fishing: Adverse effects on local fishing activities, crucial for the community’s livelihood.
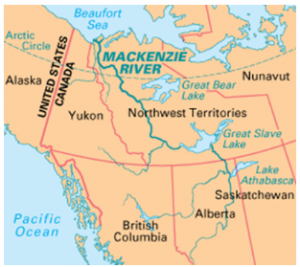
About the Mackenzie River
- Location: Canada, flowing through the Northwest Territories.
- Length: Longest river system in Canada, approximately 1,650 km (1,025 miles).
- Origin: Great Slave Lake.
- Mouth: Empties into the Beaufort Sea in the Arctic Ocean.
- Historical Significance:
- Transportation: Key route for transportation.
- Natural Resources: Vital for the exploitation of natural resources.
-
Daily Current Affairs - 28th November 2024
-
Daily Current Affairs - 27th November 2024
-
Daily Current Affairs - 25th November 2024
-
Daily Current Affairs - 23rd November 2024
-
Daily Current Affairs - 22nd November 2024
-
Daily Current Affairs - 21st November 2024
-
Daily Current Affairs - 20th November 2024
-
Daily Current Affairs - 19th November 2024
Categories
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 | 31 | |||||